In today's digitally connected world, businesses and individuals require a robust and scalable infrastructure to support their applications and services. Amazon Web Services (AWS), the leading cloud computing platform, stands out with its unparalleled global infrastructure. In this blog post, we will delve into the technical details that make AWS global infrastructure a powerhouse, enabling businesses to achieve unprecedented levels of scalability, reliability, and performance.
Regions and Availability Zones:
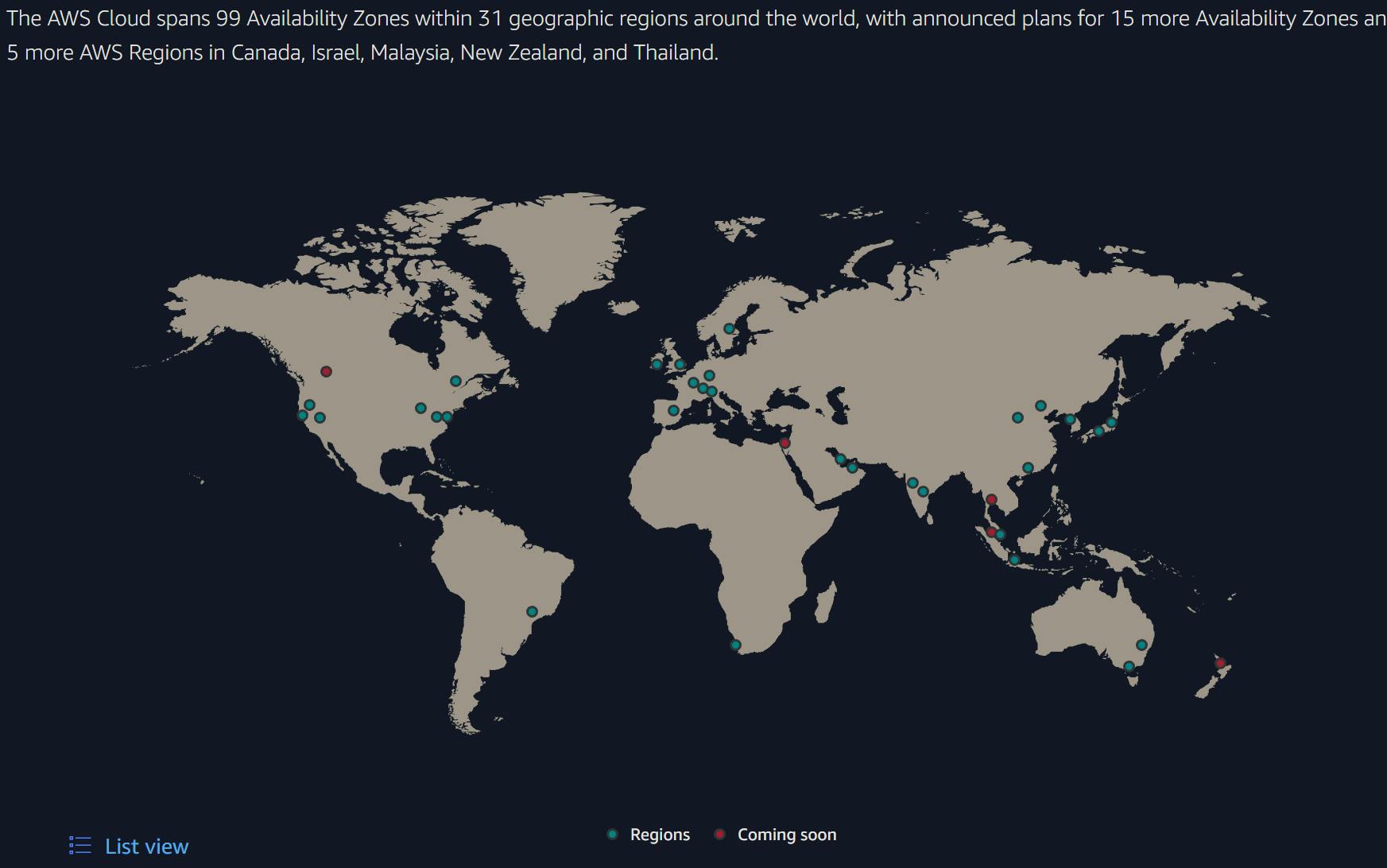
AWS operates in multiple geographic regions spread across the globe. These regions are strategically located to ensure proximity to users and compliance with data sovereignty requirements. Each region consists of multiple Availability Zones (AZs), which are physically separate data centers designed to provide fault tolerance and high availability. Currently, AWS boasts 31 regions globally, with 99 AZs, ensuring customers can deploy their applications in close proximity to their end-users while maintaining resilience. This distributed infrastructure allows businesses to design their systems with geographic redundancy, ensuring continuity even in the face of natural disasters or other regional disruptions. Each AZ within a region is connected through low-latency, high-bandwidth links, enabling synchronous data replication and facilitating reliable inter-AZ communication.
AWS DATACENTERS

Edge Locations and Content Delivery
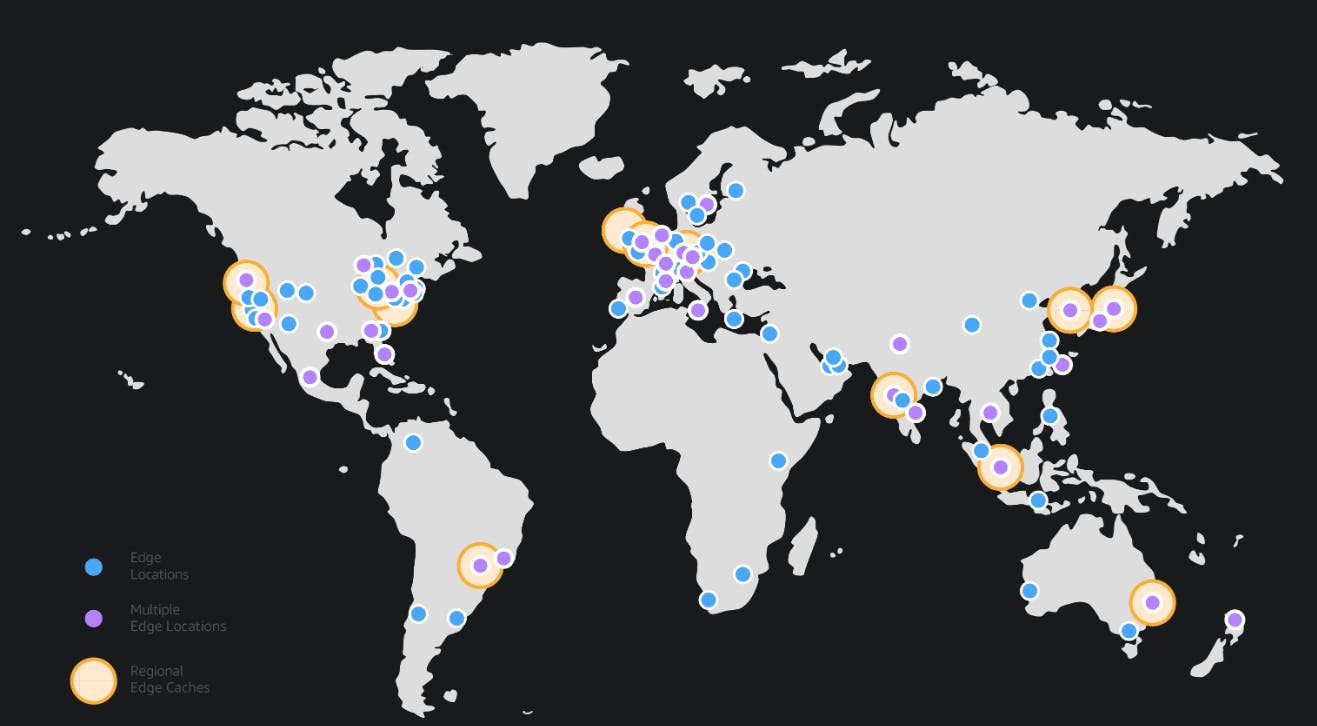
To minimize latency and enhance the delivery of content to end-users, AWS has established a vast network of Edge Locations. These Edge Locations serve as endpoints for AWS's Content Delivery Network (CDN) service, Amazon CloudFront. CloudFront is designed to efficiently deliver static and dynamic content with ultra-low latency and high data transfer speeds. With over 250 Edge Locations strategically placed around the world, AWS can cache content closer to end-users, reducing the distance data needs to travel. This caching mechanism ensures faster access to content, resulting in improved user experiences, especially for media streaming, websites, and applications with global user bases. CloudFront also provides advanced capabilities such as dynamic content caching, real-time content updates, and intelligent routing, further optimizing content delivery.
Networking and Connectivity
AWS global infrastructure boasts a robust and highly interconnected network, enabling seamless communication between different regions, Availability Zones, and Edge Locations. The AWS global network is built on a high-speed, low-latency fiber-optic backbone, with redundant connections to ensure reliability and fault tolerance. This global network allows businesses to establish private, secure, and high-performance connections across their infrastructure components. Through services like Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (VPC), businesses can create isolated virtual networks within the AWS infrastructure. VPC provides granular control over network settings, allowing businesses to define subnets, configure routing tables, and establish network access control policies. This level of control ensures secure and efficient communication between different components of an application or service deployed on AWS.
AWS Direct Connect is another critical service that enables businesses to establish dedicated network connections between their on-premises data centers and AWS regions. These private connections bypass the public internet, providing higher bandwidth, lower latency, and improved security. AWS Direct Connect offers different connection speeds and provides a direct link between the customer's network and AWS, allowing for seamless integration of on-premises infrastructure with AWS services. This connectivity enables businesses to extend their existing infrastructure to the cloud seamlessly while maintaining security and compliance requirements.
Elasticity and Scalability
One of the key advantages of AWS global infrastructure is its ability to scale resources dynamically to meet fluctuating demands. AWS provides a wide range of services, such as Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) and Amazon Relational Database Service (RDS), that can be easily provisioned or deprovisioned based on workload requirements. EC2 instances can be quickly launched, resized, or terminated, allowing businesses to scale their compute capacity up or down as needed, without significant upfront costs or infrastructure investments. Similarly, RDS provides managed database services that can be scaled vertically or horizontally to handle varying workloads, ensuring optimal performance and cost efficiency.
In addition to manual scaling, AWS offers auto-scaling features that automatically adjust the number of EC2 instances or the capacity of other services based on predefined rules and metrics. This dynamic scaling capability allows businesses to optimize costs, ensure consistent performance during peak usage periods, and accommodate sudden spikes in traffic. With features like load balancing and application autoscaling, businesses can distribute workloads across multiple instances and automatically adjust resources based on demand. This elastic infrastructure empowers organizations to respond quickly to changing business needs and scale their resources up or down as necessary.
High Availability and Disaster Recovery
AWS has designed its global infrastructure with a strong focus on high availability and disaster recovery. By leveraging the inherent redundancy of multiple Availability Zones within a region, businesses can architect fault-tolerant solutions that withstand even the most challenging circumstances. Applications and services can be deployed across multiple Availability Zones, ensuring that if one zone experiences an outage or failure, the others can continue to operate seamlessly. AWS offers various services and features to facilitate high availability, such as Elastic Load Balancing, which distributes incoming traffic across multiple instances or Availability Zones to ensure workload balance and fault tolerance.
In addition to regional redundancy, AWS provides services and features that support robust disaster recovery strategies. For example, Amazon S3 (Simple Storage Service) provides highly durable object storage that automatically replicates data across multiple facilities within a region. This redundancy ensures that even in the event of hardware failures or natural disasters, data remains accessible and protected. Amazon S3 also offers cross-region replication, allowing businesses to replicate data to a different region for further resilience. This replication process occurs automatically, ensuring data durability and availability across multiple geographic locations.
AWS provides additional services to facilitate disaster recovery planning and execution. Amazon Glacier offers long-term archival storage with low-cost retrieval options, making it suitable for backup and data archiving purposes. AWS Backup provides a centralized, fully managed backup solution that automates backup scheduling, retention management, and restoration of resources across various AWS services. Furthermore, AWS provides tools like AWS CloudFormation and AWS CloudTrail, which enable businesses to create and manage infrastructure as code and capture detailed logs and audit trails for compliance and troubleshooting purposes.
Beneath the Waves: How Submarine Cables Connect AWS to the World
In addition to its impressive global infrastructure, AWS relies on a fascinating system of underwater cables known as submarine cables to connect its data centers and services across the globe. These super-sized cables stretch across oceans, similar to the internet cables that connect your home to the web. Their purpose is to facilitate the transmission of data between continents, playing a crucial role in bridging geographical gaps.
Submarine cables are constructed using special fibers that carry data in the form of light signals. These fibers are designed to withstand the harsh conditions of the ocean, including immense pressure and the corrosive nature of saltwater. They function as hidden highways under the sea, silently enabling the interconnectedness of the world.
AWS has made significant investments in building and maintaining a network of submarine cables. These cables ensure that data can travel swiftly and securely between locations, whether it's for sending emails, streaming videos, or utilizing cloud-based applications. By leveraging these submarine cables, AWS delivers fast and reliable access to its cloud services worldwide. This means that businesses and individuals can seamlessly connect, collaborate, and innovate on a global scale, regardless of their physical location.
Next time you use AWS services, take a moment to appreciate the role played by these underwater cables. They work diligently beneath the ocean waves, connecting continents and powering your digital experiences. Through their silent efforts, they keep you connected to the vast and ever-expanding digital world.
Key AWS Services Recap
Amazon CloudFront: Global content delivery network (CDN) service with Edge Locations for fast and reliable content delivery.
AWS Direct Connect: Dedicated network connection service for establishing secure, high-bandwidth links between on-premises infrastructure and AWS.
Amazon S3: Highly durable and scalable object storage service with cross-region replication for data backup and long-term archival.
Amazon Glacier: Low-cost storage service for long-term data archival.
AWS CloudFormation: Infrastructure as code service for automating resource provisioning and management.
AWS CloudTrail: Service for capturing detailed logs and audit trails to ensure compliance and enable troubleshooting.
Elastic Load Balancing: Load balancing service for distributing traffic across instances or Availability Zones to ensure high availability and fault tolerance.
Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (VPC): Isolated virtual networks for secure communication between AWS resources and on-premises infrastructure.
AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM): Identity and access management service for managing access to AWS resources securely.
AWS Backup: Centralized, fully managed backup solution for automating backup scheduling, retention management, and restoration of AWS resources.
AWS Artifact: On-demand access to AWS compliance reports and security documentation.
Amazon Relational Database Service (RDS): Managed database service that offers scalability and automated backup features.
AWS Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2): Scalable virtual server instances that can be provisioned or deprovisioned based on workload requirements.
Amazon Route 53: Scalable domain name system (DNS) service for routing end users to applications.
AWS Lambda: Serverless computing service for running code without provisioning or managing servers.